Atoms - Chemical elements
What are Atoms
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. Everything you see, touch, and even yourself is made of atoms. So what are atoms? They are the smallest units of matter that make up the universe and everything in it.
An atom is the smallest unit into which matter can be divided without it losing its characteristic properties.
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
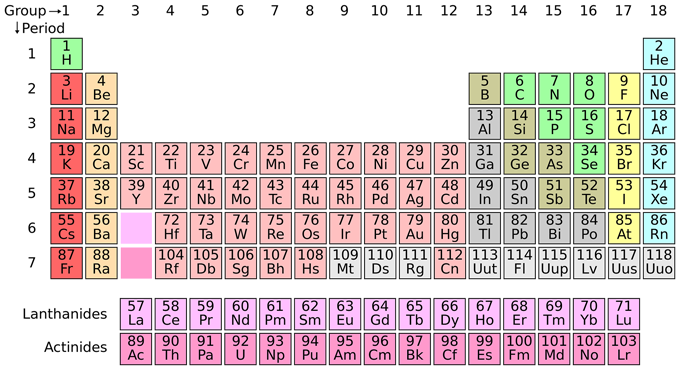
Scientists have discovered 118 types of atoms, also known as elements or chemical elements, and they have categorized them in a chart called the "Periodic Table". See below
The Subatomic Particles
Atoms are made of subatomic particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral, and electrons are negatively charged. Protons and neutrons live in the center of an atom in what is called the nucleus, which is surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged particles (electrons).
- Protons are positively charged particles that are found in the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom is unique to each element and it's what determine which type of atom it is (e.g., all atoms with 6 protons are carbon atoms, and all atoms with 26 protons are iron atoms).
The number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number, which is displayed above the element's symbol on the periodic table.
- Neutrons are subatomic particles with no charge. Neutrons are slightly larger than protons, and like protons they are found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of neutrons in a nucleus affects the mass of the atom but not its chemical properties. (e.g. a nucleus with six protons and six neutrons will have the same chemical properties as a nucleus with six protons and nine neutrons, however their masses will be different).
Atoms with the same number of protons, but have different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element, and the sum of the protons and neutrons in an atom, is called the atomic mass number.
- Electrons are negatively charged particle, that orbit around the nucleus in what is called orbital shells. Electrons are much smaller than protons and neutrons, in fact over 1,800 times smaller than either a proton or a neutron. Changing the number of electrons in an atom would create what is called an ion (electrically charged atoms).
If an atom gains one or more electrons it's called an anion (a negatively charged atom).
If an atom loses one or more electrons it's called a cation (a positively charged atom).
